Text field
Text fields let users enter text into a UI.
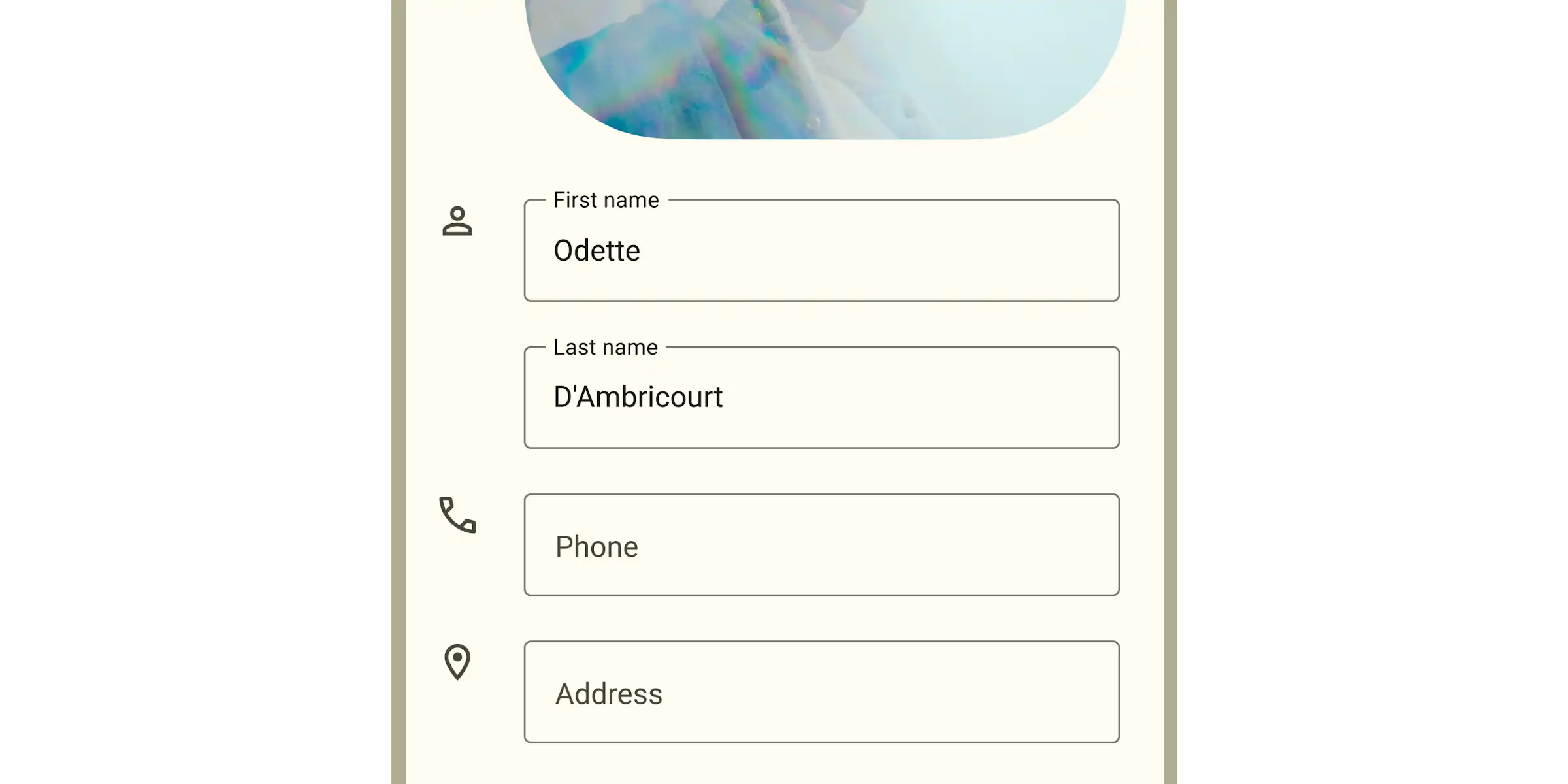
Types
Link to “Types”Interactive Demo
Link to “Interactive Demo”View interactive demo inline.
Open interactive demo in new tab.
Usage
Link to “Usage”Text fields behave like <input> elements. They provide a container with labels for user input.
<md-filled-text-field label="Label" value="Value">
</md-filled-text-field>
<md-outlined-text-field label="Label" value="Value">
</md-outlined-text-field>Input type
Link to “Input type”A text field's type attribute changes how the text field works, such as displaying a different keyboard or providing default validation.
type="text"(default)type="email"type="number"type="password"type="search"type="tel"type="url"type="textarea"
<md-filled-text-field label="Username" type="email">
</md-filled-text-field>
<md-filled-text-field label="Password" type="password">
</md-filled-text-field>star use the inputmode attribute for more control over the displayed keyboard.
Labels
Link to “Labels”Text fields should label their value with a floating label, a placeholder, or an external label. Labels help the user understand what value to input.
<md-outlined-text-field label="Favorite food">
</md-outlined-text-field>
<md-outlined-text-field placeholder="email@domain.com">
</md-outlined-text-field>
<div>First name</div>
<md-outlined-text-field aria-label="First name">
</md-outlined-text-field>bookmark text fields do not currently support aria-labelledby. External labels must provide an aria-label. See b/276484803.
Textarea
Link to “Textarea”Multi-line text fields behave like <textarea> elements.
Textareas can specify the initial number of rows. Use CSS width, height, and resize to control the resize behavior of a textarea.
<style>
md-filled-text-field {
resize: vertical;
}
</style>
<md-filled-text-field
type="textarea"
label="Vertical resize"
rows="3">
</md-filled-text-field>Icons
Link to “Icons”Text fields may display optional icons. Use icons to describe the input method (such as a search icon), provide additional functionality (such as a clear icon), or to express errors.
<md-outlined-text-field placeholder="Search for messages">
<md-icon slot="leading-icon">search</md-icon>
</md-outlined-text-field>
<md-outlined-text-field label="Password" type="password">
<md-icon-button toggle slot="trailing-icon">
<md-icon>visibility</md-icon>
<md-icon slot="selected">visibility_off</md-icon>
</md-icon-button>
</md-outlined-text-field>
<md-outlined-text-field
label="Username"
error
error-text="Username not available">
<md-icon slot="trailing-icon">error</md-icon>
</md-outlined-text-field>Prefix and suffix
Link to “Prefix and suffix”Add prefix-text and suffix-text attributes to text fields to display additional context for the value.
<md-outlined-text-field
label="Dollar amount"
type="number"
value="0"
prefix-text="$"
suffix-text=".00">
</md-outlined-text-field>Supporting text
Link to “Supporting text”Supporting text conveys additional information about the input field, such as how it will be used. Supporting text can be replaced with error text when validating.
<md-filled-text-field
label="Comments"
supporting-text="Provide comments for the issue">
</md-filled-text-field>
<md-filled-text-field
label="Name"
required
supporting-text="*required"
error-text="Please fill out this field">
</md-filled-text-field>Character counter
Link to “Character counter”Text fields with a maxlength attribute will display a character counter.
<md-outlined-text-field label="Title" value="Short" maxlength="10">
</md-outlined-text-field>Validation
Link to “Validation”Text fields that validate can use constraint validation or manual validation.
Constraint validation
Link to “Constraint validation”Text fields may validate using the browser's constraint validation API. Each input type above links to an article that describes how to validate it.
Text fields in a <form> will validate on submission, or by calling textField.reportValidity().
<form>
<md-filled-text-field
name="name"
label="Name"
required>
</md-filled-text-field>
<md-filled-text-field
name="email"
label="Email"
pattern="[\w\d-]+"
suffix-text="@gmail.com">
</md-filled-text-field>
</form>Use the following properties and methods to check and report validation errors.
validityis the text field's currentValidityState.setCustomValidity()sets a custom error message.checkValidity()dispatches aninvalidevent.reportValidity()dispatches aninvalidevent and displays the error in the text field's supporting text.
Manual validation
Link to “Manual validation”Alternatively, text fields can manually control their error state and error message. Use manual validation if the text fields are driven by application state logic.
<md-outlined-text-field
label="Username"
value="jdoe"
error
error-text="Username is not available">
</md-outlined-text-field>star Prefer constraint validation when possible for more platform features, such as <form> validation and listening to invalid events.
Accessibility
Link to “Accessibility”Add an aria-label attribute to text fields with external labels or text fields whose labels need to be more descriptive.
<div>Username</div>
<md-filled-text-field aria-label="Username"></md-filled-text-field>
<md-filled-text-field label="First" aria-label="First name"></md-filled-text-field>Filled text field
Link to “Filled text field”Filled and outlined text fields are functionally identical. See choosing a text field for guidance on which one to use.
<md-filled-text-field label="Filled" value="Value"></md-filled-text-field>Outlined text field
Link to “Outlined text field”Filled and outlined text fields are functionally identical. See choosing a text field for guidance on which one to use.
<md-outlined-text-field label="Outlined" value="Value"></md-outlined-text-field>Theming
Link to “Theming”Text fields support Material theming and can be customized in terms of color, typography, and shape.
Filled text field tokens
Link to “Filled text field tokens”| Token | Default value |
|---|---|
--md-filled-text-field-container-shape | --md-sys-shape-corner-extra-small |
--md-filled-text-field-container-color | --md-sys-color-surface-container-highest |
--md-filled-text-field-focus-active-indicator-color | --md-sys-color-primary |
--md-filled-text-field-input-text-font | --md-sys-typescale-body-large-font |
--md-filled-text-field-label-text-font | --md-sys-typescale-body-large-font |
Filled text field example
Link to “Filled text field example”<style>
:root {
--md-filled-text-field-container-shape: 0px;
--md-sys-typescale-body-large: 400 1rem system-ui;
--md-sys-color-primary: #006a6a;
--md-sys-color-surface-container-highest: #e0e3e2;
--md-filled-text-field-label-text-color: #3f4948;
--md-filled-text-field-input-text-color: #161d1d;
}
</style>
<md-filled-text-field label="Filled" value="Value">
</md-filled-text-field>Outlined text field tokens
Link to “Outlined text field tokens”| Token | Default value |
|---|---|
--md-outlined-text-field-container-shape | --md-sys-shape-corner-extra-small |
--md-outlined-text-field-focus-outline-color | --md-sys-color-primary |
--md-outlined-text-field-input-text-font | --md-sys-typescale-body-large-font |
--md-outlined-text-field-label-text-font | --md-sys-typescale-body-large-font |
Outlined text field example
Link to “Outlined text field example”<style>
:root {
--md-outlined-text-field-container-shape: 0px;
--md-sys-typescale-body-large: 400 1rem system-ui;
--md-sys-color-primary: #006a6a;
--md-outlined-text-field-label-text-color: #3f4948;
--md-outlined-text-field-input-text-color: #161d1d;
}
</style>
<md-outlined-text-field label="Outlined" value="Value"></md-outlined-text-field>MdFilledTextField <md-filled-text-field>
Link to “MdFilledTextField <md-filled-text-field>” Properties
Link to “Properties”| Property | Attribute | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
error | error | boolean | false | Gets or sets whether or not the text field is in a visually invalid state. This error state overrides the error state controlled by reportValidity(). |
errorText | error-text | string | '' | The error message that replaces supporting text when error is true. If errorText is an empty string, then the supporting text will continue to show.This error message overrides the error message displayed by reportValidity(). |
label | label | string | '' | The floating Material label of the textfield component. It informs the user about what information is requested for a text field. It is aligned with the input text, is always visible, and it floats when focused or when text is entered into the textfield. This label also sets accessibilty labels, but the accessible label is overriden by aria-label.Learn more about floating labels from the Material Design guidelines: https://m3.material.io/components/text-fields/guidelines |
noAsterisk | no-asterisk | boolean | false | Disables the asterisk on the floating label, when the text field is required. |
required | required | boolean | false | Indicates that the user must specify a value for the input before the owning form can be submitted and will render an error state when reportValidity() is invoked when value is empty. Additionally the floating label will render an asterisk "*" when true.https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Attributes/required |
value | value | string | '' | The current value of the text field. It is always a string. |
prefixText | prefix-text | string | '' | An optional prefix to display before the input value. |
suffixText | suffix-text | string | '' | An optional suffix to display after the input value. |
hasLeadingIcon | has-leading-icon | boolean | false | Whether or not the text field has a leading icon. Used for SSR. |
hasTrailingIcon | has-trailing-icon | boolean | false | Whether or not the text field has a trailing icon. Used for SSR. |
supportingText | supporting-text | string | '' | Conveys additional information below the text field, such as how it should be used. |
textDirection | text-direction | string | '' | Override the input text CSS direction. Useful for RTL languages that use LTR notation for fractions. |
rows | rows | number | 2 | The number of rows to display for a type="textarea" text field. Defaults to 2. |
cols | cols | number | 20 | The number of cols to display for a type="textarea" text field. Defaults to 20. |
inputMode | inputmode | string | '' | |
max | max | string | '' | Defines the greatest value in the range of permitted values. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#max |
maxLength | maxlength | number | -1 | The maximum number of characters a user can enter into the text field. Set to -1 for none. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#maxlength |
min | min | string | '' | Defines the most negative value in the range of permitted values. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#min |
minLength | minlength | number | -1 | The minimum number of characters a user can enter into the text field. Set to -1 for none. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#minlength |
noSpinner | no-spinner | boolean | false | When true, hide the spinner for type="number" text fields. |
pattern | pattern | string | '' | A regular expression that the text field's value must match to pass constraint validation. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#pattern |
placeholder | placeholder | string | '' | Defines the text displayed in the textfield when it has no value. Provides a brief hint to the user as to the expected type of data that should be entered into the control. Unlike label, the placeholder is not visible and does not float when the textfield has a value.https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Attributes/placeholder |
readOnly | readonly | boolean | false | Indicates whether or not a user should be able to edit the text field's value. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#readonly |
multiple | multiple | boolean | false | Indicates that input accepts multiple email addresses. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input/email#multiple |
step | step | string | '' | Returns or sets the element's step attribute, which works with min and max to limit the increments at which a numeric or date-time value can be set. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#step |
type | type | string | 'text' | The <input> type to use, defaults to "text". The type greatly changes how the text field behaves.Text fields support a limited number of <input> types:- text - textarea - email - number - password - search - tel - url See https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#input_types for more details on each input type. |
autocomplete | autocomplete | string | '' | Describes what, if any, type of autocomplete functionality the input should provide. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Attributes/autocomplete |
disabled | boolean | undefined | ||
name | string | undefined | ||
selectionDirection | string | undefined | ||
selectionEnd | number | undefined | ||
selectionStart | number | undefined | ||
valueAsNumber | number | undefined | ||
valueAsDate | Date | undefined |
Methods
Link to “Methods”| Method | Parameters | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
select | None | void | Selects all the text in the text field. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/HTMLInputElement/select |
setRangeText | args | void | |
setSelectionRange | start, end, direction | void | Sets the start and end positions of a selection in the text field. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/HTMLInputElement/setSelectionRange |
stepDown | stepDecrement | void | Decrements the value of a numeric type text field by step or n step number of times.https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/HTMLInputElement/stepDown |
stepUp | stepIncrement | void | Increments the value of a numeric type text field by step or n step number of times.https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/HTMLInputElement/stepUp |
reset | None | void | Reset the text field to its default value. |
formResetCallback | None | void | |
formStateRestoreCallback | state | void |
Events
Link to “Events”| Event | Type | Bubbles | Composed | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
select | Event | Yes | No | The native select event on <input> |
change | Event | Yes | No | The native change event on <input> |
input | InputEvent | Yes | Yes | The native input event on <input> |
MdOutlinedTextField <md-outlined-text-field>
Link to “MdOutlinedTextField <md-outlined-text-field>” Properties
Link to “Properties”| Property | Attribute | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
error | error | boolean | false | Gets or sets whether or not the text field is in a visually invalid state. This error state overrides the error state controlled by reportValidity(). |
errorText | error-text | string | '' | The error message that replaces supporting text when error is true. If errorText is an empty string, then the supporting text will continue to show.This error message overrides the error message displayed by reportValidity(). |
label | label | string | '' | The floating Material label of the textfield component. It informs the user about what information is requested for a text field. It is aligned with the input text, is always visible, and it floats when focused or when text is entered into the textfield. This label also sets accessibilty labels, but the accessible label is overriden by aria-label.Learn more about floating labels from the Material Design guidelines: https://m3.material.io/components/text-fields/guidelines |
noAsterisk | no-asterisk | boolean | false | Disables the asterisk on the floating label, when the text field is required. |
required | required | boolean | false | Indicates that the user must specify a value for the input before the owning form can be submitted and will render an error state when reportValidity() is invoked when value is empty. Additionally the floating label will render an asterisk "*" when true.https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Attributes/required |
value | value | string | '' | The current value of the text field. It is always a string. |
prefixText | prefix-text | string | '' | An optional prefix to display before the input value. |
suffixText | suffix-text | string | '' | An optional suffix to display after the input value. |
hasLeadingIcon | has-leading-icon | boolean | false | Whether or not the text field has a leading icon. Used for SSR. |
hasTrailingIcon | has-trailing-icon | boolean | false | Whether or not the text field has a trailing icon. Used for SSR. |
supportingText | supporting-text | string | '' | Conveys additional information below the text field, such as how it should be used. |
textDirection | text-direction | string | '' | Override the input text CSS direction. Useful for RTL languages that use LTR notation for fractions. |
rows | rows | number | 2 | The number of rows to display for a type="textarea" text field. Defaults to 2. |
cols | cols | number | 20 | The number of cols to display for a type="textarea" text field. Defaults to 20. |
inputMode | inputmode | string | '' | |
max | max | string | '' | Defines the greatest value in the range of permitted values. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#max |
maxLength | maxlength | number | -1 | The maximum number of characters a user can enter into the text field. Set to -1 for none. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#maxlength |
min | min | string | '' | Defines the most negative value in the range of permitted values. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#min |
minLength | minlength | number | -1 | The minimum number of characters a user can enter into the text field. Set to -1 for none. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#minlength |
noSpinner | no-spinner | boolean | false | When true, hide the spinner for type="number" text fields. |
pattern | pattern | string | '' | A regular expression that the text field's value must match to pass constraint validation. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#pattern |
placeholder | placeholder | string | '' | Defines the text displayed in the textfield when it has no value. Provides a brief hint to the user as to the expected type of data that should be entered into the control. Unlike label, the placeholder is not visible and does not float when the textfield has a value.https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Attributes/placeholder |
readOnly | readonly | boolean | false | Indicates whether or not a user should be able to edit the text field's value. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#readonly |
multiple | multiple | boolean | false | Indicates that input accepts multiple email addresses. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input/email#multiple |
step | step | string | '' | Returns or sets the element's step attribute, which works with min and max to limit the increments at which a numeric or date-time value can be set. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#step |
type | type | string | 'text' | The <input> type to use, defaults to "text". The type greatly changes how the text field behaves.Text fields support a limited number of <input> types:- text - textarea - email - number - password - search - tel - url See https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input#input_types for more details on each input type. |
autocomplete | autocomplete | string | '' | Describes what, if any, type of autocomplete functionality the input should provide. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Attributes/autocomplete |
disabled | boolean | undefined | ||
name | string | undefined | ||
selectionDirection | string | undefined | ||
selectionEnd | number | undefined | ||
selectionStart | number | undefined | ||
valueAsNumber | number | undefined | ||
valueAsDate | Date | undefined |
Methods
Link to “Methods”| Method | Parameters | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
select | None | void | Selects all the text in the text field. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/HTMLInputElement/select |
setRangeText | args | void | |
setSelectionRange | start, end, direction | void | Sets the start and end positions of a selection in the text field. https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/HTMLInputElement/setSelectionRange |
stepDown | stepDecrement | void | Decrements the value of a numeric type text field by step or n step number of times.https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/HTMLInputElement/stepDown |
stepUp | stepIncrement | void | Increments the value of a numeric type text field by step or n step number of times.https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/HTMLInputElement/stepUp |
reset | None | void | Reset the text field to its default value. |
formResetCallback | None | void | |
formStateRestoreCallback | state | void |
Events
Link to “Events”| Event | Type | Bubbles | Composed | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
select | Event | Yes | No | The native select event on <input> |
change | Event | Yes | No | The native change event on <input> |
input | InputEvent | Yes | Yes | The native input event on <input> |